Vegetable oils and fats in cosmetics - how healthy are they?
What are vegetable oils and fats?
Vegetable oils and fats consist of fatty acid esters, so-called triglycerides, as well as secondary substances such as riboflavin (vitamin B2), folic acid (vitamin B9), tocopherol (vitamin E), squalane, terpenes, minerals such as sodium, potassium, magnesium, iron and zinc [1] , as well as essential amino acids such as tyrosine, phenylalanine, leucine and lysine. Whether and how much of these substances are present varies from plant to plant.
What are triglycerides?
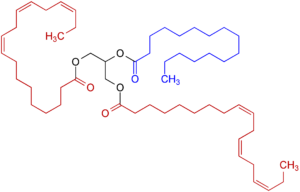
Fig.1 Triglyceride, with unsaturated fatty acids (red), saturated fatty acids (blue), and glycerin (black)
riglycerides are so-called esters of fatty acids and glycerin. They are formed by dehydration of molecules and are characterized by the fact that they bind two molecules via an oxygen. These bonds can be cleaved by acidic addition of water or by saponification to produce either the fatty acids or their fatty acid salts [2]. Triglycerides with multiple (polyunsaturated) fatty acids are more fluid, while triglycerides with low to no unsaturated fatty acids are more likely to be solid.
What are fatty acids?

Abb. 2 Lachs hat einen der größten Gehälter an Omega-3-Fettsäuren aller Nahrungsmittel
Fettsäuren sind lange Kohlenwasserstoffketten, welche mindestens eine Carbonsäuregruppe besitzen. Sie sind alle schwache Säuren und keinerlei vergleichbar mit der Säurewirkung von z.B. Salzsäure. Es gibt sehr viele, mal mehr, mal wenig unterschiedlich. Generell kann man unter „gesättigten“ und „ungesättigten“ Fettsäuren unterscheiden, hierbei stehen die Bezeichnungen für Doppelbindungen im Molekül. Fettsäuren ohne Doppelbindungen bezeichnet man als „gesättigt“, Fettsäuren mit Doppelbindungen als „ungesättigt“.
Fatty acids which are polyunsaturated are rather fluid, saturated fatty acids are rather solid [3]. The most common or most found in cosmetics fatty acids are stearic acid, palmitic acid, lauric acid, oleic acid, erucic acid, linoleic acid, arachidic acid and caproic acid [4]. Also, there are fatty acids that the body can not produce itself, yet needs such. the omega-3 fatty acid. It is one of the essential fatty acids of the body that he does not make himself, but on the food intake. They are called omega-3 fatty acids because the last double bond of the polyunsaturated fatty acid, from the carboxylic acid, is 3 carbon behind the last carbon single bond (CC) (This is called omega, since the single bond, as the omega sign in the Greek alphabet last). One such herbal omega-3 fatty acid is alpha-linolenic acid. Omega-3 fatty acids are metabolized for energy, and are used to produce so-called Series 3 prostaglandins, which are responsible for anti-inflammatory. Their metabolites are also needed to regulate blood pressure, control blood clotting and the immune system, and maintain a balanced heart rate [19].
What are the secondary substances in oils and fats?
Secondary substances in vegetable oils and fats include vitamins and minerals, e.g.
-Tocopherol, the vitamin E, which has the task in the body to protect against oxidative stress[5],
-Riboflavin, vitamin B2, which is used in metabolism as a starting material for the production of antioxidant coenzymes[6],
-Squalan, a terpene that softens and smoothes the skin[7].
Minerals are e.g.
- Potassium, which is important for the skin, kidneys, nerves and brain[8],
- Calcium, which is important for blood, teeth and bones[9],
- Magnesium, which is important for the arteries, heart and muscle[10],
- Phosphorus, which is important for teeth, bones and the brain[11],
- Iron, which is important for the blood, nails and skin[12],
- Zinc, which is a component of many enzymes, and is essential for the metabolism of sugar fat and protein[13]
What are the properties of vegetable oils and fats?

Abb. 3 Aus Kokosnüssen wird das vielseitige Kokosöl gewonnen
The triglycerides are split on the skin, releasing the fatty acids and glycerin. Many fatty acids have anti-inflammatory and protective effects against oxidative stress. In combination, they can firm the skin, strengthen the tissue, strengthen the barrier functions of the skin, protect against water loss, as well as pigmentation spots, counteract both overpigmentation and underpigmentation, and loosen cornification of the skin. They can make the hair softer and smoother and contribute to a naturally beautiful shine, and make the hair healthier overall[14].
Which oils and fats are used in cosmetics?
Frequently used oils are e.g. Jojoba, sesame, argan, avocado, almond, and apricot kernel oils, less exotic, yet often-used oils are e.g. Olive oil and rapeseed oil [15], however, these are just a few of many different oils used. Besides oils, fats and butters are also popular, e.g. Cocoa and shea butter, or coconut oil or coconut oil [16]. They all have different properties, and in the right proportions, they make cosmetics with extraordinary effects.
How are vegetable oils and fats extracted or produced?
Pflanzenöle können auf mehrere weisen gewonnen werden, so z.B. durch das Pressen von Biomasse entweder heiß oder kalt, oder durch Extraktion mit Lösemitteln. Diese Gewinnung und die darauf folgenden Aufbereitungsverfahren bestimmen die Bezeichnung und Inhaltsstoffe der Pflanzenöle. So ist ein Öl welches kaltgepresst (unter 60°C), und nicht raffiniert wurde „unraffiniert“, „kaltgepresst“ und „nativ“, wobei nativ für ein naturbelassenes Öl steht, welches noch so gut wie alle Wirkstoffe besitzt. Ein raffiniertes Öl hat im Gegensatz so gut wie gar keine Sekundärstoffe mehr. Raffinierte Öle sind weitestgehend geruchs-, und geschmackslos, jedoch sehr lange haltbar und universal einsetzbar. Unraffinierte Öle sind dahingegen weniger lange haltbar, haben jedoch ihren typischen, Geruch und Geschmack, sowie den Großteil der Sekundärstoffe behalten. Sie werden jedoch, um die Haltbarkeit zu verlängern gedämpft, wodurch ein Teil der Sekundärstoffe verloren geht. Native Öle sind kaltgepresste Öle, welche im Gewinnungsprozess keinem weiterem Schritt zur Verbesserung der Haltbarkeit durchlaufen. Sie haben noch alle Sekundärstoffe, sind dafür jedoch weniger lange haltbar[17].
Are cosmetics with vegetable oils and fats, better than those without?
Die Frage nach dem „Was ist denn jetzt besser?“ ist zu generell gefragt, schlussendlich kommt es auf jeden selbst an ob oder ob nicht. Fakt ist, dass Kosmetika mit Pflanzenölen, anstelle von Mineralölen, verträglicher und um einiges umweltschonender sind. Aus bestimmten Mischungen von Pflanzenölen kann man selbst auf hoch empfindliche Haut optimal eingehen, eine Flexibilität, welche Mineralölkosmetik nicht besitzt[18]. Möchte man sich selbst, und seiner Umwelt, etwas gutes tun, sind Pflanzenöle eine sehr gute Alternative zu Mineralölen.
Sources:
Wikipedia[1][7][17]
List of the most important trace elements and their uses[8][9][10][11][12][13]
Article on the effects of jojoba oil[15]
Article on the effects of almond oil[15]
Article on the effects of coconut oil [16]
Contribution to the effects of vegetable oils on the skin and hair[14][18]
List of the most important vitamins and their benefits[5][6]
Contribution to the chemistry of triglycerides[2]
Scientific article on fatty acids[3][4]
Scientific article on omega-3 fatty acids[19]




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!