Glucocorticoids - What are they and why are they in cosmetics?
What are glucocorticoids?
Glucocorticoids (GCC for short) are steroid hormones that our body produces in the adrenal cortex. It fulfills many important purposes in the body and is found too often in medicines and partly in cosmetics[1].
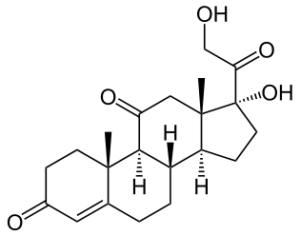
Fig. 1 The cortisone
What are GCC chemically and what do they do in the body?
GCC are steroid hormones, ie analogues to hormones. The "Gluco" in their name is due to their use in glucose metabolism. In doing so, they contribute to the breakdown of protein (proteins) into glucose, thus they are protein-splitting hormones. They affect the metabolism, water and electrolyte balance, the cardiovascular and the nervous system, they also have anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive, i. Suppressing immune system reaction. Cortisone and cortisol are among the most important of these GCCs, with cortisone being the inactive form of cortisol[2].
Why are they in medicines and cosmetics?
GCC have strong anti-inflammatory properties, which is why they are used in ointments and tablets. For example, Cortisone used against swelling, inflammation and diseases such as hives[3].
Are there any side effects?
With short, personally adjusted quantity prescription no side effects are to be expected. Short overdose can cause dizziness, headache, depression or psychosis. Prolonged use of overdoses can lead to more severe symptoms such as osteoporosis, increased blood sugar levels, or even impotence. After a longer intake, one should not suddenly stop taking the preparation, because the body has put down its own production or even turned it off completely and needs a certain amount of time to normalize it again[4].
Are there any alternatives for the topical application?
For products with topical application, so creams, ointments and the same, there are some alternatives for the treatment of swelling, redness, irritation and itching, so the body's natural defense functions. For example, Extracts of marigold, sea buckthorn, aloe vera and propolis. There is also the Bromelain, an extract of enzymes from the pineapple, which, similar to cortisone, decomposes proteins[5].
1. Marigold: The Marigold is used both internally and externally against ulcers and injuries. Burns, wounds, redness, irritation and more are quickly cured by marigold extracts.
This is mainly due to high levels of flavonoids, up to 0.9%, various saponoids, essential oils from sesquiterpenes, triterpenes, coumarins and polysaccharides[6].
2. Seabuckthorn: Sea buckthorn looks great internally and externally. It boosts the regeneration and healing of wounds, and its anti-inflammatory properties make itching and redness go away quickly. However, the oil and pulp are very expensive as the fruits grow on bushes densely covered with thorns.
Diese Effekte sind den Inhaltsstoffen zu danken, so mit unter hohen Mengen an Vitamin C, B, E und A. Ebenfalls enthält es viele Mineralstoffe wie Eisen, Magnesium und Kalium[7].
3. Aloe Vera: Everyone has heard of the wonder drug Aloe Vera, the desert lily. It heals wounds, insect bites and sunburns through its antibacterial and cooling effect. It also protects the body from parasites, fungi and bacteria from within.
The reason is not surprising, with over 200 active ingredients such as vitamins, enzymes, minerals and amino acids, Aloe Vera is prepared for anything[8].
4. Propolis: Not for the vegan lifestyle, but a true marvel of wildlife. Propolis is a bee product and can be freely translated to "out of town" or "for the city". Bees use it to keep fungi, bacteria and viruses out of their sticks. It has anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antibacterial and antifungal effects and is therefore a miracle cure for wound healing.
For this, the bees work rather hard though. They collect resins from trees, mostly conifers, store them in pollen sacs, and mix it with wax and pollen [9].[9].
5. Bromelain: Bromelain findet sich in der Ananas, und wird häufig gegen starke Schwellungen eingesetzt. Es ist ein Enzymgemisch, welches es vermag Eiweiß zu spalten (ähnlich dem Cortisol). Durch diese Eigenschaft kann es bei Entzündungen eingesetzt werden, sowohl als auch durch seine Beeinflussung auf die Blutgerinnung, Schwellungen und Ödeme nach Operationen vermindern. Manche Menschen haben allergische Reaktionen auf Bromelain, und sollten es deshalb nicht zu sich nehmen[10].
–
Sources:
Wikipedia[1][3]
Professional article on cortisone in medicine[2][4]
Article about sea buckthorn[7]